The world around us is filled with various shapes, ranging from simple and two-dimensional to intricate and multi-dimensional. Among these, 3D shapes hold a special interest. These shapes exist in three dimensions: length, width, and height.
This article aims to cover definitions, types, formulas to calculate their volume and surface area, real-life applications, and examples to better understand this topic.
What is a 3 dimensional shape?
A 3 dimensional shapes are geometric figures that occupy space and have three dimensions. These Shapes are also known as 3D shapes. These shapes exist in physical space and are not limited to flat surfaces like 2D shapes. They have volume and can be described using various properties, including edges, vertices, and faces.
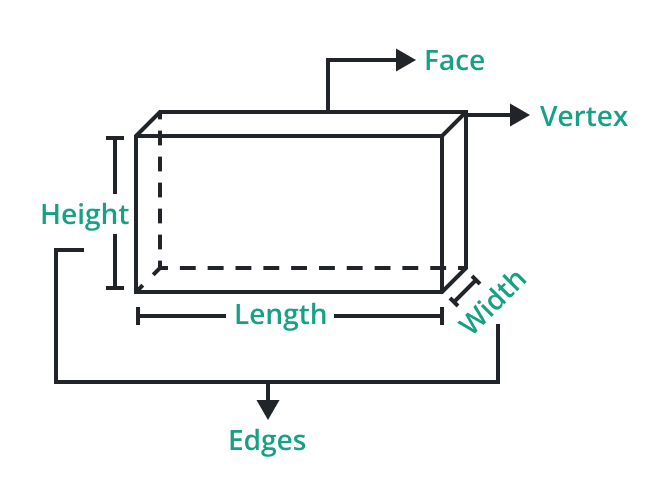
Basic properties of Three-Dimensional shapes:
Three-dimensional shapes possess unique properties that set them apart from their Two-dimensional counterparts. These properties include:
- Volume
- Surface area
- Vertices, Edges, and Faces.
Let's look more closely at each of these.
Volume
A three-dimensional shape's volume is the area that it occupies in space. It is measured in cubic units and provides insight into the capacity of Shapes.
Surface Area
Unlike 2D shapes with only an area, 3D shapes have a surface area, the total area of all the surfaces that make up the shape.
Vertices, Edges, and Faces
These terms describe the structural components of three-dimensional shapes.
- Vertices are the corners where edges meet.
- Edges are the lines connecting vertices.
- Faces are the flat surfaces that define the shape's boundaries.

Types of 3D Shapes
Three-dimensional shapes come in various forms, each with its different characteristics. Let’s Explore some common types:
Cube
A six-faced solid with all sides of equal length and all angles at 90 degrees.

Sphere
A perfectly round shape with all points on its surface equidistant from its center.

Cylinder
A shape with two parallel circular bases of equal size connected by a curved surface.

Cone
A shape with a circular base and a single curved surface that tapers to a point called the apex.

Prism
A shape with two parallel and congruent polygonal bases connected by rectangular or parallelogram faces.

Pyramid
The shape with a polygonal base and triangular faces that converge at a single point is called the apex.

Torus
A shape resembling a donut, characterized by its circular cross-section and hole in the center.

Rectangular Parallelepiped
A six-faced shape with all angles at 90 degrees, and opposite faces being congruent rectangles.

Ellipsoid
A three-dimensional oval shape resembling a stretched or squashed sphere.

Octahedron
A shape with eight triangular faces and six vertices.

How to Calculate the Volume and Surface Area of Three-Dimensional Shapes?
Calculating the volume and surface area of 3D shapes is crucial for various fields. Let’s dive into how to perform this calculation for common shapes:
Shape | Volume Formula | Surface Area Formula |
Cube | V = side length³ | A = 6 × side length² |
Sphere | V = (4/3) × π × radius³ | A = 4 × π × radius² |
Cylinder | V = π × radius² × height | A = 2 × π × radius² + 2 × π × radius × height |
Cone | V = (1/3) × π × radius² × height | A = π × radius × (radius + slant height) |
Rectangular Prism | V = length × width × height | A = 2 × (length × width + width × height + height × length) |
Triangular Prism | V = (1/2) × base × height × length | A = base × height + 2 × (length × side) + 2 × (base × side) |
Pyramid (Regular) | V = (1/3) × base area × height | A = base area + 1/2 × perimeter × slant height |
Torus | V = 2 × π² × R × r² (major and minor radii) | A = 4 × π² × R × r (major and minor radii) |
Ellipsoid | V = (4/3) × π × a × b × c (semi-axes) | No simple formula; usually requires numerical integration |
Examples of Three-dimensional Shapes
Let's explore some solved examples of calculating the volume and surface area of three-dimensional shapes:
Example 1:
Find the volume of a cylinder with a radius of 3 units and a height of 8 units.
Solution:
Given Data:
Radius (r) = 3 units
Height (h) = 8 units
Formula:
Volume of Cylinder = π × r² × h
Volume = π × (3²) × 8 = 72π cubic units
You can use our cylinder volume calculator to find the cylinder's volume quickly.
Example 2:
Calculate the surface area of a cone with a radius of 6 units and a slant height of 10 units.
Solution:
Given Data:
Radius (r) = 6 units,
Slant height (l) = 10 units
Formula:
Surface Area of Cone = π × r × (r + l)
Surface Area = π × 6 × (6 + 10) = 96π square units
Our surface area calculator will help you to solve the problems related to finding surface areas of different shapes.
Example 3:
Calculate the surface area of a sphere with a radius of 9 units.
Solution:
Given Data:
Radius (r) = 9 units
Formula:
Surface Area of Sphere = 4 × π × r²
Surface Area = 4 × π × (9²) = 324π square units
Applications of the 3-D shapes:
Three-dimensional shapes find practical applications in numerous fields. Here are some examples:
Architecture and Engineering
- Architects use 3D models to design buildings and structures.
- Engineers use 3D shapes to design bridges, roads, and other infrastructure.
Manufacturing and Product Design
- Manufacturing processes often involve creating components with specific 3D shapes, ensuring proper fit and function in products.
- Product designers use 3D modeling software to create prototypes and test the aesthetics and ergonomics of items before production.
Medicine and Medical Imaging
- Medical imaging technologies such as MRI and CT scans create 3D representations of internal organs and structures, aiding in diagnoses and surgical planning.
- Prosthetics and implants are designed using 3D modeling to ensure precise fits and improved patient outcomes.
Geography and Mapping
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) use 3D shapes to model terrain, urban landscapes, and environmental changes for urban planning and environmental studies.
Automotive Industry
- Car designers use 3D modeling to create vehicle designs, considering aerodynamics, aesthetics, and structural integrity.